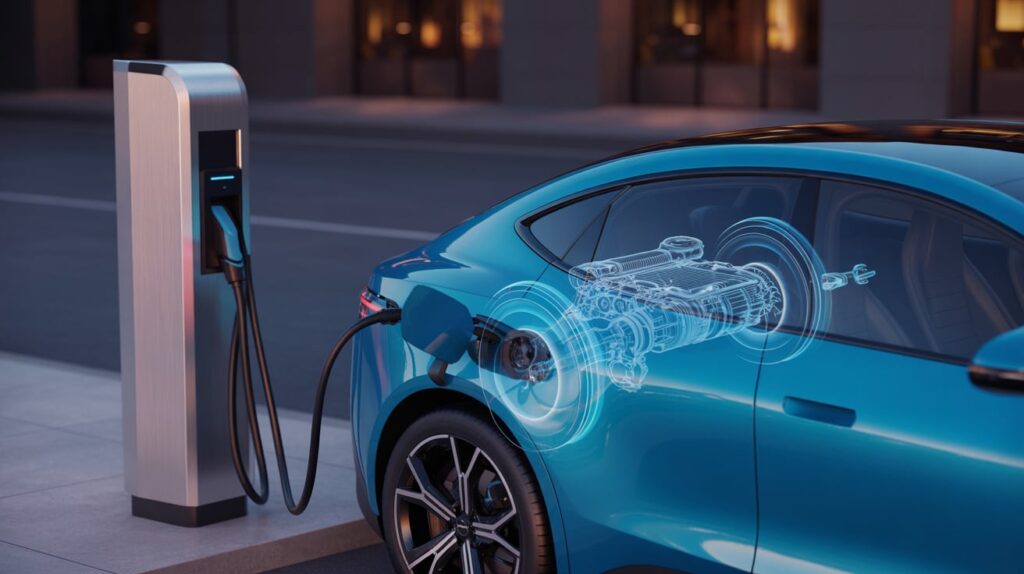

When I first started researching electric cars, one question kept coming up – do electric cars have engines? The answer might surprise you. Electric cars don’t have traditional engines at all. Instead, they use electric motors that work completely differently from what you’ll find under the hood of gas-powered cars.
This distinction isn’t just technical jargon. Understanding how electric cars work helps you make better decisions about your next vehicle purchase. Whether you’re considering a Tesla, BMW electric car, or any other EV, knowing the difference between motors and engines changes everything.
In this guide, I’ll break down exactly how electric cars work, why they don’t need traditional engines, and what this means for you as a driver. By the end, you’ll understand why electric vehicles are gaining popularity and how they compare to conventional cars.
What Makes Electric Cars Different from Regular Cars
The biggest difference between electric cars and gas cars lies in how they create motion. Regular cars use internal combustion engines that burn fuel to create power. Electric cars use electric motors that convert electricity directly into motion.
Here’s what makes each system unique
Traditional Car Engines
Gas-powered cars rely on internal combustion engines with hundreds of moving parts. These engines work by-
- Mixing air and fuel in cylinders
- Igniting the mixture with spark plugs
- Converting the explosion into rotational motion
- Transferring power through complex transmission systems
This process involves many steps and creates heat, noise, and emissions as byproducts
Electric Car Motors
Electric vehicles utilize one or more electric motors that transform electrical energy from the battery into mechanical power. The process is much simpler-
- Electric current flows from the battery to the motor
- Magnetic fields inside the motor create rotation
- Power goes directly to the wheels with minimal energy loss
- No combustion, no emissions, no complex transmission needed
The technical term matters here. Motors run on electricity and engines run on combustion. This isn’t just semantics – it reflects completely different technologies
How Electric Motors Work in EVs
I’ve had the chance to drive several electric cars, and the smooth, quiet operation always impresses me. This smoothness comes from how electric motors work
Electric motors use electromagnetic principles discovered over 150 years ago. When electric current flows through wire coils in a magnetic field, it creates rotational force. Modern EV motors refine this basic principle with-
- High-strength permanent magnets
- Precisely controlled current flow
- Advanced cooling systems
- Computer-controlled timing
The result is instant torque delivery. In an EV, instant torque is generated by an electric current and magnetic fields in the electric motor, whereas a gas engine takes much longer to combust gas and turn the crankshaft.
This instant response explains why electric cars feel so quick when accelerating from a stop
Key Components of Electric Vehicles
Modern electric cars have fewer major components than gas cars. The main parts include-
Battery Pack – Usually lithium-ion batteries that store electrical energy. Most EV batteries are located under the floor for better weight distribution.
Electric Motor – Converts electrical energy to mechanical motion. Many EVs have multiple motors for better performance and all-wheel drive
Inverter – Converts DC power from the battery to AC power for the motor. Also controls motor speed and direction
Onboard Charger – Converts AC power from charging stations to DC power for the battery
Power Electronics Controller – Acts like the brain of the EV, managing power flow and vehicle systems
Transmission – Most EVs use single-speed transmissions since electric motors provide power across a wide speed range
This simpler design means fewer things can break. Electrical vehicles usually require less repairs, since the number of parts they use is much less when compared to an internal combustion engine
Types of Electric Vehicles Available in 2025
The electric car market in 2025 offers more choices than ever before. Here are the main categories-
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
These are pure electric cars with no gas engine at all. Popular examples include-
- Tesla Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y
- BMW iX, i4, iX3
- Hyundai Ioniq 5, Ioniq 6
- Ford Mustang Mach-E
- Volkswagen ID.4
BEVs rely entirely on their electric motors and battery packs
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
These combine an electric motor with a small gas engine. They can run on electricity alone for short distances, then switch to hybrid mode. Examples include-
- Toyota Prius Prime
- BMW X5 xDrive45e
- Volvo XC60 Recharge
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
Traditional hybrids like the Toyota Prius use both an electric motor and gas engine but can’t plug in to charge. The electric motor assists the gas engine for better fuel economy
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
These use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity for electric motors. Currently limited options include the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo
Popular Electric Car Models and Their Motors
Different electric cars use different motor configurations. Here’s what I’ve learned about popular models-
Tesla Electric Cars
Tesla uses AC induction motors in most models, switching to permanent magnet motors in some newer versions. The Model S Plaid has three motors – one front, two rear – producing over 1,000 horsepower.
BMW Electric Cars
BMW’s electric vehicles like the iX and i4 use permanent magnet synchronous motors. The BMW iX has two motors providing all-wheel drive and up to 516 horsepower.
Hyundai Electric Cars
The Hyundai Ioniq 5 and upcoming Ioniq 9 use permanent magnet motors. The Ioniq 5 can have single or dual motor configurations depending on the trim level.
Ford Electric Cars
The Ford Mustang Mach-E uses permanent magnet motors, while the F-150 Lightning pickup truck has dual motors for all-wheel drive capability.
Other Notable EVs
- Chevrolet Bolt EV – Single permanent magnet motor
- Nissan Leaf – AC synchronous motor
- Volkswagen ID.4 – Rear-mounted permanent magnet motor
- Rivian R1T/R1S – Four individual motors, one per wheel
Advantages of Electric Motors Over Engines
After driving both gas and electric cars extensively, I can tell you the differences are significant. Electric motors offer several advantages-
Efficiency
Electric motors convert electricity to motion three times more efficiently, in energy terms, than the internal-combustion engine does with gasoline. This translates to lower operating costs.
Instant Torque
Electric motors deliver maximum torque immediately. Gas engines need to rev up to reach peak torque, making EVs feel quicker in everyday driving
Quiet Operation
Electric motors run almost silently compared to combustion engines. This creates a more peaceful driving experience
Fewer Moving Parts
Generating motion through the combustion process being more complex, a combustion engine therefore has many more parts and takes up more space than an electric engine.
Lower Maintenance
Without oil changes, spark plugs, timing belts, or complex transmissions, EVs need less maintenance.
Environmental Benefits
Electric motors produce no direct emissions. Even accounting for electricity generation, EVs typically have lower carbon footprints than gas cars.
Common Misconceptions About Electric Car Motors
Many people misunderstand how electric cars work. Let me clear up some common myths-
Myth 1- Electric cars are just golf carts Modern EVs use sophisticated motors with advanced control systems. Many can accelerate faster than sports cars
Myth 2- Electric motors are weak Electric motors can be incredibly powerful. The Tesla Model S Plaid makes over 1,000 horsepower from its electric motors
Myth 3- You can’t drive long distances Many new EVs have over 300 miles of range. The charging infrastructure is expanding rapidly across the US
Myth 4- Electric cars are more expensive to maintain Actually, EVs typically cost less to maintain due to fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes
Myth 5- Cold weather kills electric cars While range decreases in cold weather, modern EVs have thermal management systems to minimize this effect
Electric Car Charging and Infrastructure
Since electric cars don’t have gas engines, they need different “fuel” – electricity. The charging infrastructure has grown dramatically.
Types of Charging
Level 1 Charging – Standard 120V household outlet, very slow Level 2 Charging – 240V outlet, charges most EVs overnight DC Fast Charging – High-speed charging for road trips
Charging Networks
Major networks include Tesla Supercharger, Electrify America, ChargePoint, and EVgo. Many gas stations are adding electric car chargers
Home Charging
Most EV owners charge at home overnight. This is often the most convenient and cost-effective option
Cost Comparison – Electric Motors vs Gas Engines
The financial differences between electric and gas powertrains are significant-
Purchase Price
Electric cars often cost more upfront, but federal tax credits up to $7,500 can reduce this gap. Many states offer additional incentives
Operating Costs
Electricity costs less than gasoline per mile in most areas. The average American spends about $1,400 annually on gas, while electricity for an EV typically costs $500-800 per year.
Maintenance Costs
EVs typically save $1,000-2,000 annually on maintenance compared to gas cars
Insurance
Electric car insurance can be higher due to vehicle costs, but some insurers offer EV discounts
The Future of Electric Motors in Cars
The electric car industry is evolving rapidly. Here’s what I see coming-
Solid-State Batteries
Next-generation batteries will charge faster and provide longer range
More Efficient Motors
New motor designs will squeeze even more performance from each kilowatt
Wireless Charging
Some EVs will charge wirelessly through electromagnetic induction
Vehicle-to-Grid Technology
EVs will be able to power homes and feed electricity back to the grid
Autonomous Driving
Electric platforms are ideal for self-driving technology integration
Best Electric Cars for Different Needs
Based on current options and upcoming 2025 models-
Best Overall EV
Tesla Model 3 – Great range, performance, and charging network
Best Luxury EV
BMW iX – Premium interior, advanced technology, solid range
Best Electric SUV
Hyundai Ioniq 5 – Spacious, fast-charging, competitive price
Best Budget EV
Chevrolet Bolt EV – Affordable price, decent range
Best Electric Truck
Ford F-150 Lightning – Practical, powerful, can power your house
Best Family EV
Volkswagen ID.4 – Roomy interior, good safety ratings, reasonable price
Environmental Impact of Electric Motors
Electric motors themselves produce zero direct emissions. The environmental impact depends on how the electricity is generated
In areas with clean electricity grids, EVs have much lower carbon footprints than gas cars. Even in this worst-case scenario, an EV still uses around one-third less energy than gasoline, referring to regions with coal-heavy electricity.
As the US electrical grid gets cleaner with more renewable energy, EVs become even more environmentally friendly.
Maintenance Differences Between Electric and Gas Cars
The maintenance differences between electric motors and gas engines are dramatic-
Electric Car Maintenance
- Brake pad replacement (less frequent due to regenerative braking)
- Tire rotation and replacement
- Cabin air filter replacement
- Battery coolant system checks
- Software updates
Gas Car Maintenance
- Oil changes every 3,000-7,500 miles
- Spark plug replacement
- Air filter replacement
- Transmission service
- Timing belt replacement
- Fuel system cleaning
- Exhaust system repairs
The simpler electric drivetrain eliminates most of these maintenance needs
Frequently Asked Questions
Do electric cars have engines?
No, electric cars do not have traditional internal combustion engines. Instead, they use electric motors that convert electrical energy from batteries into mechanical motion to move the vehicle.
What’s the difference between an electric motor and an engine?
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical motion using electromagnetic principles. An engine burns fuel (like gasoline) to create combustion that produces mechanical energy. Motors are generally more efficient and have fewer moving parts.
How many motors do electric cars have?
Electric cars can have one, two, three, or even four motors depending on the design. Single-motor EVs are typically rear-wheel drive, while dual-motor EVs offer all-wheel drive. Some high-performance EVs like the Tesla Model S Plaid have three motors.
Are electric motors more powerful than gas engines?
Electric motors can produce more torque instantly compared to gas engines, which makes them feel more powerful during acceleration. However, total horsepower can vary widely between different electric and gas vehicles
Do electric cars need transmissions?
Most electric cars use single-speed transmissions because electric motors can efficiently operate across a wide speed range. This is much simpler than the multi-speed transmissions needed for gas engines.
How long do electric car motors last?
Electric motors typically last longer than gas engines because they have fewer moving parts and don’t experience combustion stress. Many manufacturers warranty EV motors for 8-10 years or 100,000+ miles.
Can electric car motors be repaired?
Yes, electric motors can be repaired, but they’re generally more reliable than gas engines. Most issues involve the electronic control systems rather than the motor itself
Do electric cars make noise?
Electric motors run very quietly compared to combustion engines. EVs are so quiet that newer models are required to make artificial noise at low speeds for pedestrian safety.
How efficient are electric motors compared to gas engines?
Electric motors are typically 85-95% efficient at converting energy into motion, while gas engines are only about 25-30% efficient. This efficiency difference is one reason why EVs cost less to operate.
What happens if an electric car motor fails?
If an electric motor fails, the car will need to be towed to a qualified service center. However, motor failures are relatively rare compared to gas engine problems. Many EVs have dual motors, so one motor failure might still allow limited driving capability
Conclusion
So, do electric cars have engines? The answer is definitively no. Electric cars use electric motors instead of internal combustion engines, and this difference matters more than you might think
Electric motors offer instant torque, quieter operation, better efficiency, and lower maintenance compared to traditional engines. As someone who has driven both types extensively, I can tell you the driving experience is noticeably different
The electric car market in 2025 offers more choices than ever, from affordable options like the Chevrolet Bolt to luxury vehicles like the BMW iX. With improving battery technology, expanding charging infrastructure, and falling prices, electric cars are becoming practical for more Americans
Whether you’re considering a Tesla, Ford Mustang Mach-E, or any other EV, understanding that these vehicles use motors instead of engines helps explain their unique characteristics. The future of transportation is electric, and now you understand why
If you’re thinking about making the switch to electric, consider your driving needs, available charging options, and local incentives. The technology has matured to the point where electric cars can meet most people’s transportation needs while offering a cleaner, quieter, and often more enjoyable driving experience.

Melanie Lopez is a passionate content specialist at American National Car Insurance, dedicated to simplifying car insurance for every American driver. With years of industry expertise, she crafts informative and engaging articles to help users make confident insurance decisions.